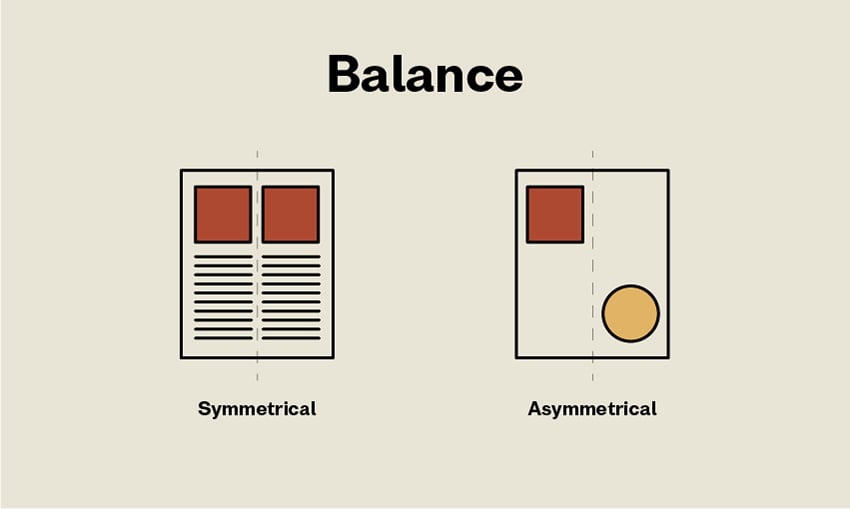
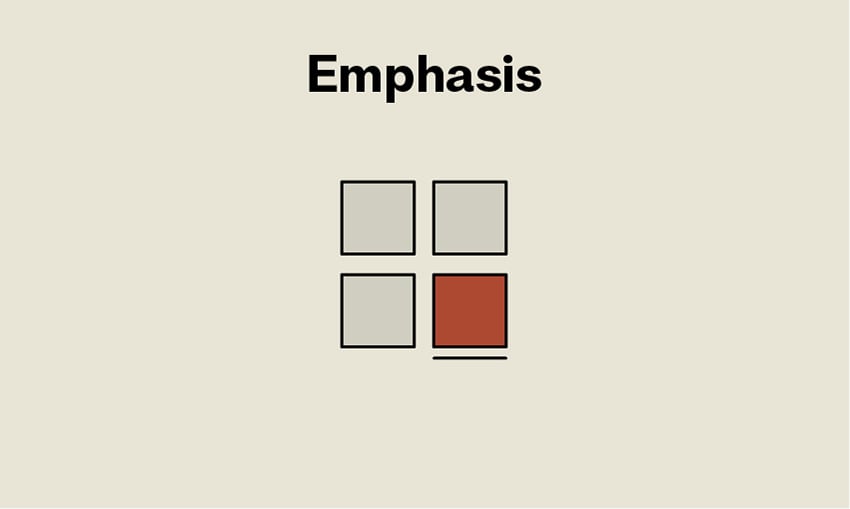
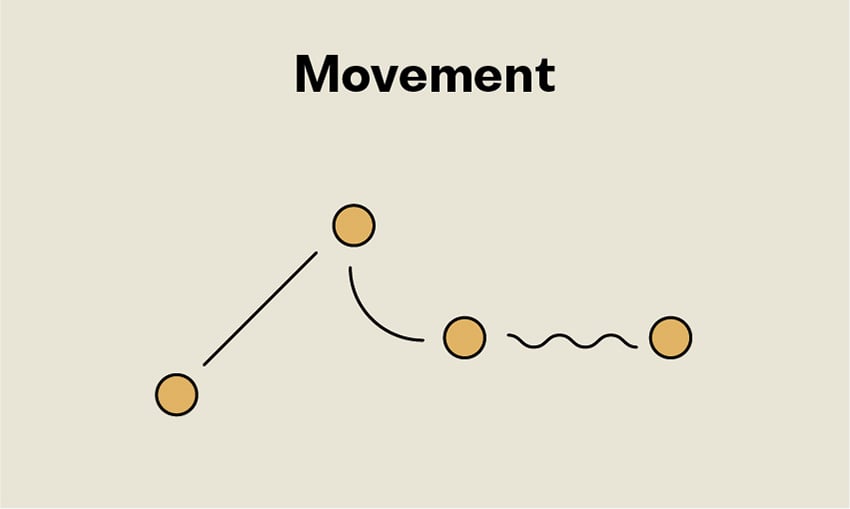
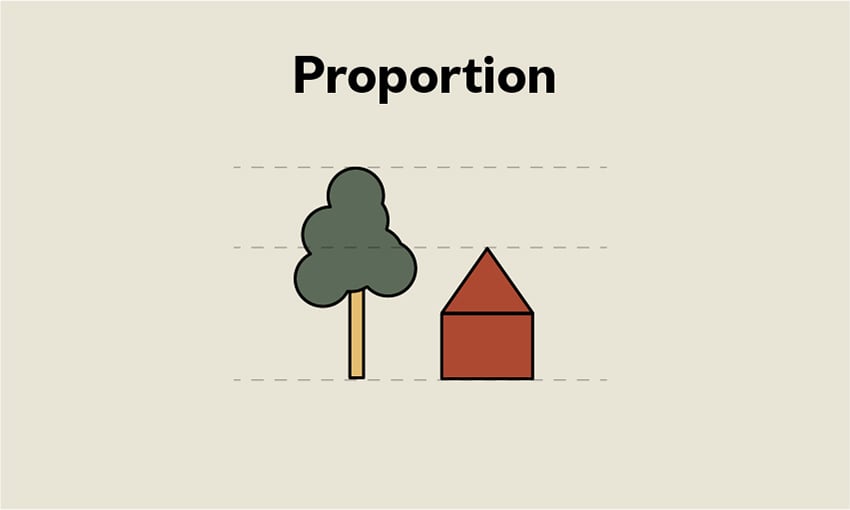
Art and Architecture
As far as history goes back, art and architecture have always been interrelated disciplines. From the elaboration of the Baroque movement to the geometric framework of Modernism, architects found inspiration from stylistic approaches, techniques, and concepts of historic art movements, and translated them into large-scale habitable structures.